Mucolipidosis II (I Cell Disorder) Market
Mucolipidosis II, commonly referred to as I Cell Disease, is a genetic condition that impairs the body’s capacity to metabolize specific cellular substances. This disorder is considered rare. The accumulation of waste products within cells can give rise to a variety of symptoms and health complications. This article delves into the various aspects of Mucolipidosis II, including its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
The root cause of Mucolipidosis II can be attributed to genetic mutations in the GNPTAB gene. This gene is responsible for producing an enzyme that facilitates the breakdown of specific substances within cells. In cases where the enzyme malfunctions, certain substances tend to build up within the cells, thereby disrupting their regular functioning. Inheritance of Mucolipidosis II occurs in an autosomal recessive manner, necessitating the acquisition of two copies of the mutated GNPTAB gene from both parents for the condition to manifest in a child.
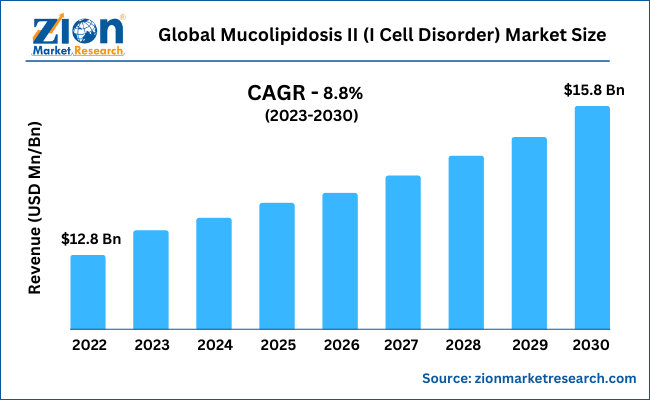
With a CAGR of nearly 8.8% between 2023 and 2030, the global mucolipidosis II (I Cell Disorder) market is expected to grow from its 2022 valuation of $12.8 Billion to reach $15.8 Billion by the end of 2030.
Mucolipidosis II symptoms typically manifest during the early stages of infancy. The severity of symptoms can vary greatly and may encompass:
Abnormal skeletal development is a condition characterized by various physical abnormalities such as short stature, reduced head size, and bone deformities in the chest, pelvis, and spine.
Mucolipidosis II can cause developmental delays in infants, hindering their ability to reach important milestones like sitting up, crawling, and walking.
Mucolipidosis II is a condition that may manifest in infants with distinct facial abnormalities. These features may include a broad nose and widely spaced teeth, resulting in a coarse appearance.
Joint stiffness is a common symptom experienced by infants diagnosed with Mucolipidosis II. This condition can cause limited mobility due to the stiffness in their joints.
Children diagnosed with Mucolipidosis II are prone to recurrent infections as a result of their weakened immune system.
Mucolipidosis II is commonly diagnosed by conducting a thorough physical examination, reviewing the patient’s medical history, and performing genetic testing. In the event that Mucolipidosis II is suspected in a child, a healthcare provider may conduct a blood test to determine the presence of heightened levels of specific substances within cells. Confirmation of a Mucolipidosis II diagnosis can be achieved through genetic testing, which involves the identification of mutations in the GNPTAB gene.
Mucolipidosis II is a condition for which there is currently no known cure. As such, the primary focus of treatment is on symptom management and the prevention of complications. Possible treatment options that may be considered include:
Physical therapy is a beneficial treatment option for children diagnosed with Mucolipidosis II. This therapy can aid in enhancing mobility and minimizing joint stiffness, ultimately improving the child’s overall physical function.
In cases of Mucolipidosis II, surgical intervention may be required to address bone or spinal malformations in pediatric patients.
In order to alleviate symptoms such as respiratory problems, seizures, and pain, healthcare professionals may recommend the use of medications.
Children diagnosed with Mucolipidosis II may necessitate supportive care to alleviate symptoms and enhance their quality of life. This may include the use of breathing assistance or feeding tubes.
At present, there are ongoing investigations into novel treatment options for Mucolipidosis II, including enzyme replacement therapy and gene therapy. These experimental therapies are being explored by researchers in the field.
Market Segments
The global market for mucolipidosis II (I cell disorder) is split up according to different symptoms, such as deafness, hypotonia, abnormal spine curvature, rapid progression of mental retardation, stunted development of both gross and fine motor abilities, and others. The gross and fine motor skills subsegment, which accounted for over a quarter of the global market share in 2022, is expected to maintain its dominance even during 2023-2030 despite its slow growth. Children with mucolipidosis II (I cell condition) often fail to acquire their gross and fine motor abilities after birth, which contributes to the segmental increase over the following eight years.
Antibiotics, experimental medicines, hip replacement, physical therapy, and others make up different subsets of the global mucolipidosis II (I cell disease) market. In 2022, antibiotics were the most popular treatment option, and this trend is expected to continue during the projection period. Antibiotic use to treat mucolipidosis II (I cell disorder) in developing countries may contribute to the market’s future expansion.
The worldwide market for treatments for mucolipidosis II (I cell condition) is broken down by end-user into specialized healthcare facilities, home healthcare providers, hospitals, and others.
Be First to Comment