The active ingredients of usually utilized sunscreens flow into the bloodstream at much greater levels than existing US standards from health regulators and necessitate further safety research, as per a small study performed by researchers of the US FDA. The OTC products initially marketed to avoid sunburn with modest regulation are broadly utilized to obstruct the sun’s radiation that can lead to skin cancer, the most ordinary malignancy in the US.
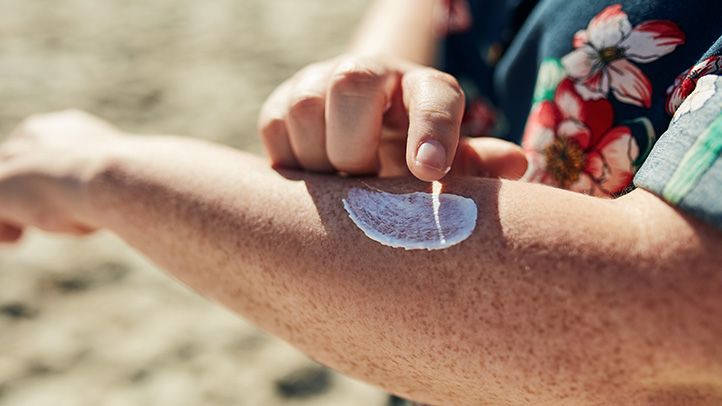
The study of 23 participants examined 4 sunscreens, comprising lotion, cream, and sprays, applied to 75% of the body 4 times daily over 4 Days, along with blood tests to verify the utmost levels of specific chemicals taken up into the bloodstream performed over 7 Days. The research discovered the chemicals’ utmost plasma levels it examined for— octocrylene, oxybenzone, avobenzone, and in one sunscreen ecamsule—to be over the level of 0.5 ng/mL upon which FDA standards demand further safety testing.
The products used in the study were not named by the researchers. The impact of plasma concentrations surpassing the FDA’s cap is not recognized and requires to be further examined, mentioned the research team. The findings in no means propose that people should discontinue utilizing sunscreen to defend against the harmful UV rays of the Sun, said the scientists.
Likewise, Haereticus Environmental Laboratory located in Virginia has been prominent in the study into toxicity of chemical sunscreen. Scientists from the lab have just issued a study in the Reproductive Toxicology signifying a connection between exposure to oxybenzone and the development of birth defects during pregnancy’s first trimester—particularly, a defect known as Hirschsprung’s Disease. The study authors stoutly advise pregnant women to shun utilizing sunscreen products in their first trimester with oxybenzone, also women endeavoring to conceive, as the chemical is fat-soluble, which can remain in the body for weeks.

Be First to Comment